Polyethylene and polypropylene raw material production process is relatively similar, products can be used to make plastic film, injection products, plastic pipe, etc., in many cases we found that the two raw materials in the nature and use of a great similarity.
But in fact, polypropylene and polyethylene raw materials in the use of a lot of differences, small make up for you to analyze the performance of polypropylene and polyethylene characteristics, to explore the difference in the material properties of different proportions of mixing.
PE and PE
Performance difference
From the point of view of heat resistance analysis, the heat resistance of polypropylene is higher than polyethylene, usually, the melting temperature of polypropylene than polyethylene higher about 40%-50%, about 160-170℃, so the product can be sterilized in 100℃ above the temperature, under the condition of no external force, 150℃ is not deformation.
In the life we can discover "5" the polypropylene meal box is often used in microwave oven heat food (the general temperature of microwave oven heat is in 100-140℃), and polyethylene is bad because of heat resistance can not be used as microwave oven with plastic, including meal box, plastic wrap.
Similarly, in the field of ordinary packaging film, polyethylene packaging bags are more suitable for the use of 90℃ below, and polypropylene packaging bags in the relatively high temperature can be used.
From the perspective of rigidity and tensile strength, polypropylene is mainly characterized by low density, better mechanical properties than polyethylene, and has a very prominent rigidity, for example, polypropylene has gradually launched the competition with engineering plastics (PA/PC), widely used in the field of electronics, electrical appliances, automotive.
At the same time, due to the high tensile strength and good bending resistance of polypropylene, it is known as "hundred fold adhesive", which is bent in half for one million times and does not change the white of the bend, which also provides a clue for us to identify polypropylene products, and at the same time becomes a hidden mark for the recycling and classification of products.
From the perspective of low temperature resistance, the low temperature resistance of polypropylene is weaker than that of polyethylene, the impact strength at 0℃ is only half of that at 20℃, and the brittle temperature of polyethylene is generally below -50℃.
With the increase of the relative molecular mass, the lowest temperature can reach -140℃.
Therefore, if the product needs to be used in a low temperature environment, or to choose polyethylene as the raw material.
Generally refrigerated food trays are made of polyethylene raw materials.
From the perspective of aging resistance, the aging resistance of polypropylene is weaker than that of polyethylene. The structure of polypropylene is similar to that of polyethylene, but it is easier to be oxidized and degraded under the action of ultraviolet light and heat due to the existence of a methyl side chain.
In daily life, the most common polypropylene products that are easy to age are woven bags, which are easy to break under the sun for a long time.
In fact, although polyethylene aging resistance is higher than polypropylene, but compared with other raw materials, its performance is not very outstanding, because in the polyethylene molecule contains a small number of double bond and ether bond, its weather resistance is not good, sun, rain will also cause aging.
From the point of view of flexibility analysis, polypropylene although the strength is higher, but the flexibility is poor, the technical point of view is poor impact resistance.
So when used to make film products, its application field and the application field of polyethylene is still different, polypropylene film is more used for surface packaging printing.
And in the aspect of pipe material, also very rarely USES the simple polypropylene to carry on the production, needs to use the crosslinked polypropylene, also is the common PPR tube.
Because the impact resistance of ordinary polypropylene is poor, easy to break, so in the actual application to add impact modifier, in the bumper and other applications to use additives to improve the impact resistance.
PE and PE
Blending performance
The impact of PE type on the impact performance of blending system
Different types of PE can improve the impact strength of PP at room temperature, but the difference is very obvious.
For PP/HDPE blends, when the HDPE mass fraction is lower than 60%, the blend strength is basically unchanged.
When the HDPE mass fraction is above 60%, the impact strength of the blends increases.
For PP/LDPE blends, only when the mass fraction of LDPE is higher than 60% can the impact strength be greatly improved.
For PP/LLDPE blends, when the mass fraction of LDPE is more than 40%, the impact strength is obviously increased.
When the LLDPE mass fraction reaches 70%, the impact strength of the blend is 37.5kj /m2, which can reach 20 times of the impact strength of pure PP, 10 times and 4 times of the PP/HDPE and PP/LDPE blends with the same dosage.
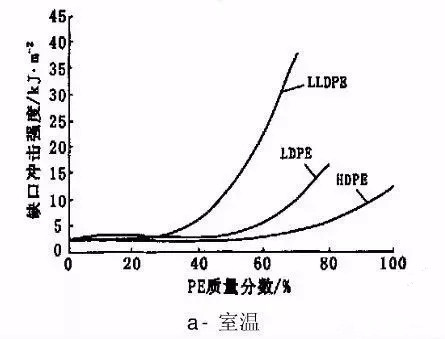
At low temperature (-18℃), the improvement trend of PP toughness of three types of PE is consistent with that of normal temperature, and LLDPE has the best toughening effect on PP.
When the mass ratio of PP/LLDPE is 30/70, the impact strength of the blend system is 23.2kj /m2, which is 20 times that of pure PP, while the impact strength of PP/HDPE and PP/LDPE blends is only about 5kJ/m2 under the same conditions.
This further indicates that when the same impact strength is reached, the amount of LLDPE is the least, which means that the rigidity of PP can be maintained more.
At the same dosage, LLDPE modified PP has the best impact strength, which makes the material obtain better toughness.
Effect of mixing method on toughening effect
The samples mixed with twin screw extruder had the highest impact strength, while those obtained by direct injection had the worst impact performance.
Because the effective length of the screw of the injection machine is less than that of the extruder, the shearing mixing effect is small, and the effect is of course very bad.
Under different mixing modes, the impact properties of the materials show the same law, that is, the mass fraction of LLDPE starts from 40%, and with the increase of the amount of LLDPE, the impact strength increases greatly.
It is shown that the mixing mode has an effect on the impact performance of the blending system, but the law remains unchanged.
Internal structure of PP/LLDPE blend
When the LLDPE mass fraction is less than 50%, the impinged section of the blending system is smooth and flat, showing typical brittle fracture characteristics.
When the LLDPE mass fraction exceeds 50%, the material section shows the characteristics of ductile fracture, with filamentous body, uneven section, tearing marks, and the two-phase interface tends to be fuzzy. At this time, the yield strength of the material increases rapidly.
When the amount of LLDPE increases to 70%, it can be clearly seen that the PP is interwoven into a net, so the material has a high impact strength on the macro level.
The size of pure PP spherulites is large and the interface between the spherulites is clear, so the impact performance of PP is extremely poor.
By contrast, LLDPE's crystals are very fine and the interface between the crystals is very fuzzy, so its impact performance is very good.
The difference in crystal morphology between PP and LLDPE is caused by the different crystallization rates: the crystallization rate of PP is slow (3.3x102nm /s), the crystal growth is large, and the crystal connections are few, so the intercrystal interface is clear.
The crystallization rate of LLDPE is very fast (8.3x102nm /S), the crystal is small, and there are many connections between crystals, so the intercrystal interface is fuzzy.
When LLDPE is added to PP, it can be obviously observed that the size of PP spherulite decreases and the interface between the crystals becomes fuzzy, which is conducive to improving the impact performance of the material.
The amount of LLDPE increases, and the spherulite of PP further decreases. When the mass fraction of LLDPE reaches 70%, the PP crystal has been divided into fragments, and the interface between the crystals completely disappears, so it is difficult to distinguish them. Therefore, the impact strength of the blending system is very high, and it is not easy to be broken.
This indicates that the addition of LLDPE refines the spherulites of PP and increases the connection between the crystals, which is another important reason for improving the toughness of the blend materials.
Influence of LLDPE dosage on blending effect
With the increase of LLDPE dosage, the yield stress of the blending system decreases, while the elongation at break increases gradually, showing a good linear relationship.
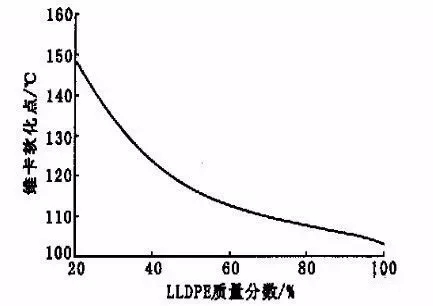
With the increase of LLDPE dosage, the softening point of vica decreased.
When the LLDPE mass fraction is 40%-60%, the softening point of vica is still close to 120 degrees.
With the increase of LLDPE dosage, the impact strength of the material increases, while the tensile yield strength, tensile modulus and vica softening point decrease.
In the system dominated by LLDPE, when the material is impacted, LLDPE phase consumes a lot of energy and improves the toughness of the material. Besides, because of LLDPE's insertion, segmentation and refinement of PP spherulites, the crystal size of PP is reduced and intercrystal connections are increased, thus improving the impact strength of the material.
In PP/LLDPE blending system, when the mass fraction of ll-dpe is 40%-70%, the blends gradually form an interpenetrating network structure with the characteristics of rigidity and toughness.


